Exploring Analytical Ferrography

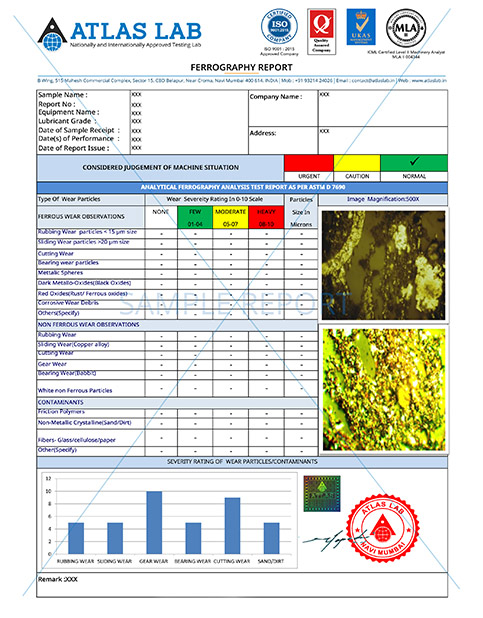
Ferrography analysis is a diagnostic technique used to analyze the wear debris and contaminants present in lubricating oils and fluids. By employing magnetic fields, this method separates and collects microscopic particles from the fluid, allowing for a detailed examination of their size, shape, composition, and concentration. Ferrography testing provides valuable insights into the condition of machinery and helps identify potential sources of wear, aiding in predictive maintenance and enhancing equipment reliability.
Unveiling the Advantages of Ferrography testing
Ferrography testing offers several advantages in the field of predictive maintenance and machinery analysis. Some of the key benefits include:
- Early Detection of Wear: Ferrography analysis can detect wear particles at a microscopic level, allowing for the identification of wear mechanisms at an early stage.
- Source Identification: The analysis of wear debris collected through ferrography helps pinpoint the source of wear, such as gears, bearings, or other components.
- Trend analysis: By conducting regular ferrography oil analysis over time, trends in wear patterns and particle concentration can be observed.
- Cost-effective maintenance: Ferrography helps in optimizing maintenance schedules, ensuring that maintenance activities are performed when needed, thereby reducing unnecessary maintenance costs.
- Improved equipment reliability: By identifying and addressing wear-related issues proactively, ferrography analysis contributes to enhancing overall equipment reliability.
- Contamination Analysis: It can identify and quantify contaminants, such as dirt, water, and other foreign particles, which can negatively impact machinery performance.
- Improving Lubrication Practices: By analyzing wear debris and contaminants, ferrography oil analysis helps optimize lubrication practices, ensuring proper lubricant selection and usage.
- Machinery Health Assessment: Regular ferrography analysis serves as a valuable tool for assessing the overall health of critical machinery and monitoring the effectiveness of maintenance programs.
- Root Cause Analysis: When combined with other diagnostic techniques, ferrography testing aids in root cause analysis of equipment failures, leading to effective problem-solving.
Inside the Lab: Interpreting the process of ferrography analysis
Sample Collection:The first step is to collect a representative sample of the lubricating oil or hydraulic fluid from the equipment being monitored.
Filtration: The collected sample is then filtered to remove any large particles or impurities that could interfere with the analysis.
Depositing onto a Slide: A portion of the filtered sample is then placed onto a glass slide, often using a magnetic pad or a vacuum-assisted deposition device.
Magnetic Field Application: A magnetic field is applied to the slide, which causes ferromagnetic wear particles (particles attracted to magnets) in the oil to align in characteristic patterns.
Fixation and Staining: The sample on the slide is fixed and stained using a dye or staining solution, enhancing the visibility of wear particles under a microscope.
Microscopic Examination: The slide is then examined under a microscope at various magnifications. The analyst identifies and classifies different wear particle types, such as abrasive, adhesive, or fatigue wear.
Quantitative Analysis: The analyst quantifies the wear particles by counting and sizing them. This data helps determine the severity of wear and the type of wear mechanisms present.
Interpretation and Reporting: Based on the microscopic examination and analysis, the analyst interprets the findings and prepares a detailed report, including information about wear rates, wear mechanisms, contamination levels etc.
Trend Monitoring: Regularly performing the ferrography test allows for trend monitoring, enabling the detection of changes in wear rates or contaminant levels over time.
Revealing The Spectrum: Different Types of Particles Identified via Ferrography
- Dirt: Distinguishes abrasive dirt particles from wear debris by size, shape, and magnetic characteristics.
- Sand: Separates sand particles based on size, shape, and their unique response to the magnetic field.
- Different Types of Metals: Classifies various metal wear particles according to their composition, size, and magnetic properties.
- Fibers: Identifies elongated fibers in the sample through morphology and magnetic behaviour.
- Regulatory compliance: Coconut oil testing is often required to comply with regulatory standards and labeling requirements set by government authorities. By conducting these tests, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the legal requirements and provide accurate information to consumers.
- Other Non-metallic Debris: Characterizes different non-metallic particles based on morphology and their interaction with the magnetic field.
- Different Types of Metals: Classifies various metal wear particles like iron, steel, copper, aluminium, bronze, brass, nickel, led, tin and silver according to their composition, size, and magnetic properties.
From Manufacturing to Aviation: Exploring Ferrography's Wide-Spanning Impact and Applications Across Industries
- Manufacturing Industry: Detecting wear in manufacturing equipment like gears, bearings, and hydraulic systems to optimize maintenance and prevent costly downtime.
- Aerospace Industry: Monitoring wear in aircraft engines, gearboxes, and hydraulic systems to ensure safe and efficient operations.
- Automotive Industry: Analyzing wear in engines, transmissions, and drivetrains to enhance vehicle performance and reliability.
- Power Generation Industry: Assessing wear in turbines, generators, and power transmission systems for reliable electricity production.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Analyzing wear in drilling equipment, pumps, and compressors to optimize production and avoid costly failures.
- Heavy Machinery Industry: Detecting wear in construction equipment, mining machinery, and industrial machinery for improved safety and productivity.
- Railways: Monitoring wear in locomotives and rail infrastructure to ensure smooth and safe rail operations.
- Wind Energy Industry: Assessing wear in wind turbines to maximize energy production and minimize maintenance costs.
Atlas Lab: Your Trusted Partner for Comprehensive Ferrography Testing and Analysis
Atlas Lab’s ferrography testing services combine cutting-edge technology with unmatched expertise, to deliver the most reliable analysis for your industrial equipment. We employ a powerful technique for identifying and assessing wear particles and debris in lubricating fluids. With a team of highly skilled engineers and technicians, we pride ourselves on our ability to detect early signs of equipment degradation, preventing potential failures and minimizing downtime.
We utilize advanced microscopy and spectroscopy tools to analyse fluid samples and accurately identify the type and size of wear particles present in your machinery. Our meticulous and detailed reports offer actionable insights, guiding you to make informed maintenance decisions that can extend the lifespan of your equipment and improve productivity. Whether you operate in the automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, or any other industry relying on critical machinery, Atlas Lab is your trusted partner for oil analysis ferrography services, ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your assets.
Don't leave your equipment's health to chance; let us provide the expertise and precision you need to keep your operations running smoothly.




